Calcium-Lipopolysaccharide-Complex-induced Cell Degeneration and cytoprotective Effects of Pramipexole, Fructose and DHEA
Ines Niehaus
Contact to: Ines_Niehaus@gmx.de)
ePoster Presentation at the
9th Congress of the German Interdisciplinary
Association
of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine
in Hamburg, Germany, 2008
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are negatively charged amphiphilic molecules with a hydrophobic Lipid A and a hydrophilic polysaccharide part. The negatively charged phosphate and carboxylgroups of 2-Keto-desoxy-octuronacid (KDO) in the Lipid A of the LPS monomers are bridging with Ca2+-ions to uni- and multilamellar vesicles. A high concentration of Ca2+-ions is available at voltaged-gated calcium-channels in nerve and muscle cells. Ca2+-ions at the calcium-channels are complexed by LPS and the polysaccharide chains of calcium-channels bind to the oligosaccharide chains of LPS, which leads to partely or completely blocking of calcium-channels with inability of the channels to pump sufficient concentrations of Ca2+-ions into the cell inspite of the increased energy-ATP-consumption of the cell. This is shown electrophysiologically by LPS-induced conduction block in animal experiments and one case report. Electrophysiologically measurements are showing a chronically normocalcemic tetany with muscle cramps and periodically occuring conduction blocks at voltages of <= -70mV provoking a hypotonic transient paralysis and at voltages of >= + 30 mV provoking a hypertonic stiff paralysis in a case report describing a chronically endotoxemia after a contamination with 10 microgram Salmonella minnesota S-LPS. Furthermore, the cerebral glucose and dopamine metabolism is reduced with oedematic swelling and gliosis in the patient. The neuronal conduction block is probably caused by the blocking of the calcium-channels induced by the LPS-aggregates. LPS will be uptaken intracellularely via endocytosis by e. g. intercalation in vesicles filled with neurotransmitters. LPS is binding to membranes of the cell including Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The intraneuronal binding of LPS to ER is impairing the vesicle transport of e. g. neurotransmitters, which causes insoluble protein-LPS-aggregates coaggregated to neurofibrilles. Furthermore, LPS is stimulating the phospholipase C with intracellularely increased Ca2+-values leading to oedematic swelling of the cells. Complexes of Ca2+-ions with fructose-1,6-biphosphate are probably binding to LPS aggregates, which is impairing the binding of Ca2+-LPS-aggregates to iono-receptors. It is also being impaired by the steroid hormone Dehydroepiandrosterone DHEA via reversible binding of DHEA to the iono-receptors. The inflammation-reducing dopamine D2-agonist pramipexole is reducing the LPS-stimulated cAMP production.


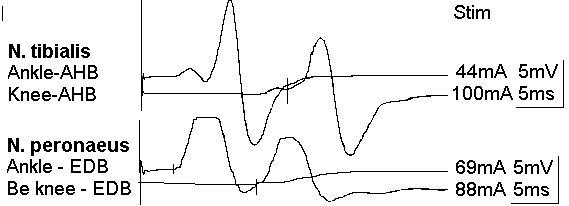
Electrophysiology: LPS-induced polyneuropathy and encephalopathy
Results of a 34 yrs old female patient 11 years after contamination with
Salmonella minnesota S-LPS. Encephalopathy is described by parkinsonism and reduced
glucose metabolism of the cerebral cortex.
More information to the case report:
http://www.s-lps.de/artikel3.html
>


Activation of voltage-gated calcium channels and how conduction blocks might be caused by lipopolysaccharides in the nervous system


Bindung of LPS to voltage-gated calcium channels


The pentapeptide lysine-tyrosine-phenylalanine-glutamine-phenylalanine of the
alpha2-delta2-subunit of calcium channels probably binds to lipid A of LPS.
Lipid A of E. coli binds to the pentapeptide lysine-phenylalanine-serine-phenylalanine-lysin.
1
The positively charged lysine binds to the negatively charged 2-Keto-desoxy-octuronacid (KDO) and phosphate of lipid A.
The second lysine molecule of the pentapeptide might not be necessary for the
binding to lipid A of Salmonella minnesota LPS because of the intramolecularely neutralized second
phosphate-group with the positively charged amino-monosaccharide (Fig.7 ).
The amino acids No. 582 to No. 604 of alpha2-delta2-subunit of calcium channels are involved in the binding of pregabaline or gabapentine to calcium channels. 2 Is pregabaline able to prevent the binding of LPS to the same pentapeptide of calcium channels and could be helpfully to prevent the neuronal conduction blocks described in the case report?
Structure of the Gram negative membrane with calcium-LPS-complexes

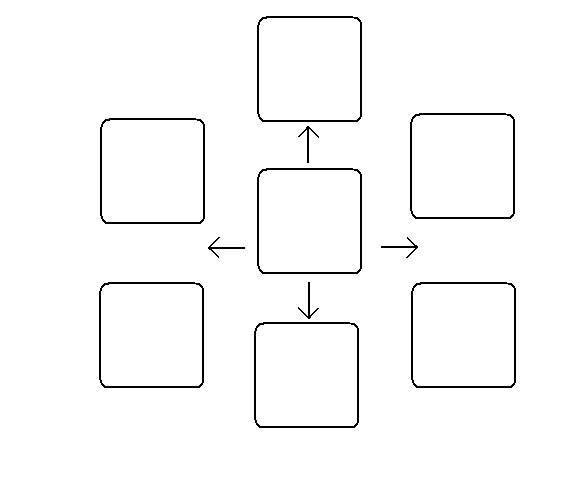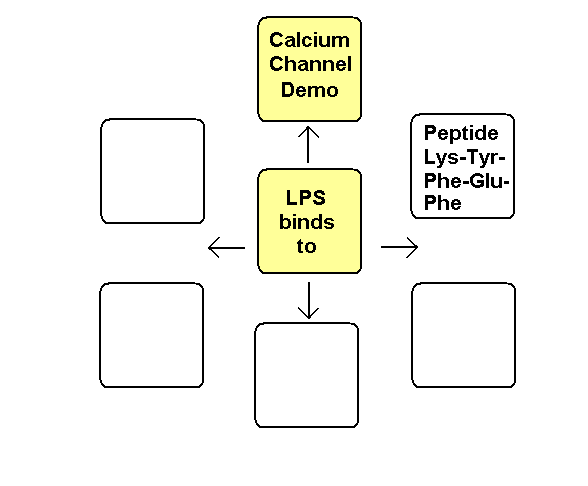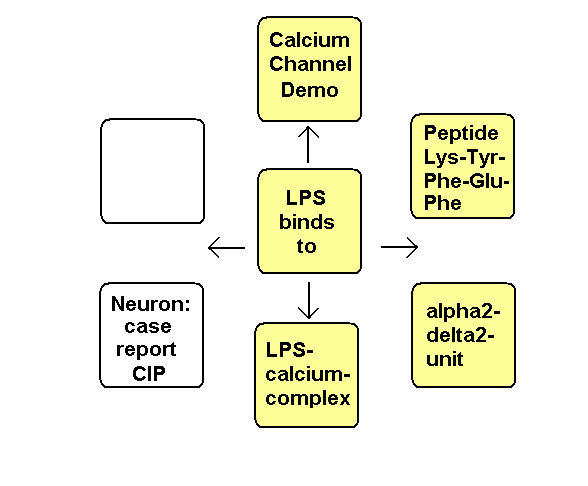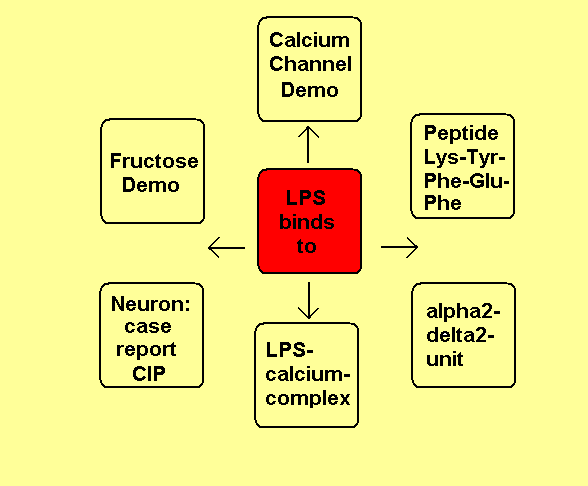
Therapy options with Fructose or Inulin

a) Bindung of LPS to calcium channels:
Negatively charged KDO and phosphate groups of Lipid A complex calcium ions. Calcium-LPS-complexes binds to alpha2-delta2subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels with the polysaccharide chains to the N-glycosylated oligosaccharide chains of the channels and with Lipid A probably to the pentapeptide Lys+-Tyr-Phe-Glu-Phe of the alpha2-delta2subunit. The antiepileptic drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are also binding to this pentapeptide sequence.
b) Conduction block:
A LPS-induced conduction block 3 might be caused by blocked calcium-influx into the neuron due to calcium-LPS-complexes binding to calcium channels. The peroneal nerve is mostly damaged in the described case report. The peroneal nerve is mostly sensitive to the concentration of LPS in the blood of septic patients. 4
c) Therapy options:
Dehydroepiandrosteron DHEA binds to the dihydropyridine-binding site of calcium channels acting like a calcium channel agonist. DHEA might also change the three-dimensional structure of Lipid A similar as fructose so that the bindung of LPS to calcium channels is more difficult. The polyfructose Inulin is reducing the uptake of endotoxin from the gut to the blood. The anti-parkinsonian agent pramipexole acts as a dopamine D2-receptor-agonist reducing the LPS-stimulated cAMP-production releasing the LPS-induced inflammation.
d) Recent News:
NADPH-Oxidase NOX5 contains starting at amino acid 737 at the C terminal end
one LPS binding pentapeptid with the amino acid sequence of
lys-phe-gly-phe-arg in opposite to NOX1-NOX4 (unpublished results).
NOX5 has 4 calcium binding so called EF hand units.
If calcium is extracellularely complexed with EDTA, NOX5 don't produce H202 from 02 and does not induce an intracellularely flow of calcium ions. NOX5 is being inhibited by a tripeptide GGF (Gly-Gly-Phe), which is a sequence occuring in enkephalins. GGF has a neuroprotective effect in femtomolar and micromolar concentrations..5
Outlook:
Leu-enkephalin with the tripeptide GGF is being used in the
described patient in Ámol concentration for treatment of critical
illness polyneuropathy with excellent first results.
More information
on treatment of septic polyneuropathy with leucine enkephalin in this case report.
References:
1)
Frecer V, Ho B, Ding JL.
Interpretation of biological activity data of bacterial endotoxins by simple
molecular models of mechanism of action.
Eur J Biochem. 2000; 267(3):837-52.
[PubMed]
[free
article]
2)
Marais E, Klugbauer N, Hofmann F.
Calcium channel alpha(2)delta subunits-structure and Gabapentin binding.
Mol Pharmacol. 2001; 59(5):1243-8.
[PubMed]
[free article]
3)
Brown RF, Jackson GD, Martin T, Westbrook RF, Pollard JD,
Westland KW.
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces a conduction block in the sciatic
nerves of rats
Lab Anim Sci. 1999; 49(1):62-9.
[PubMed]
4)
Mohammadi B, Schedel I, Graf K et al.
Role of endotoxin in the pathogenesis of critical illness
polyneuropathy.
J Neurol. 2008; 255(2):265-72.
[PubMed]
5)
Qin L, Liu Y, Qian X, Hong JS, Block ML.
Microglial NADPH oxidase is a novel target for femtomolar
neuroprotection against
oxidative stress.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005; 1053: 107-20.
[PubMed]
[free article]

The page was edited on June, 9th 2009.
Last updated: May, 8th 2010